Storage CDN
All assets uploaded to Supabase Storage are cached on a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to improve the latency for users all around the world. CDNs are a geographically distributed set of servers or nodes which cache content from an origin server. For Supabase Storage, the origin is the storage server running in the same region as your project. Aside from performance, CDNs also help with security and availability by mitigating Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) and other application attacks.
Example
Let's walk through an example of how a CDN helps with performance.
A new bucket is created for a Supabase project launched in Singapore. All requests to the Supabase Storage API are routed to the CDN first.
A user from the United States requests an object and is routed to the U.S. CDN. At this point, that CDN node does not have the object in its cache and pings the origin server in Singapore.
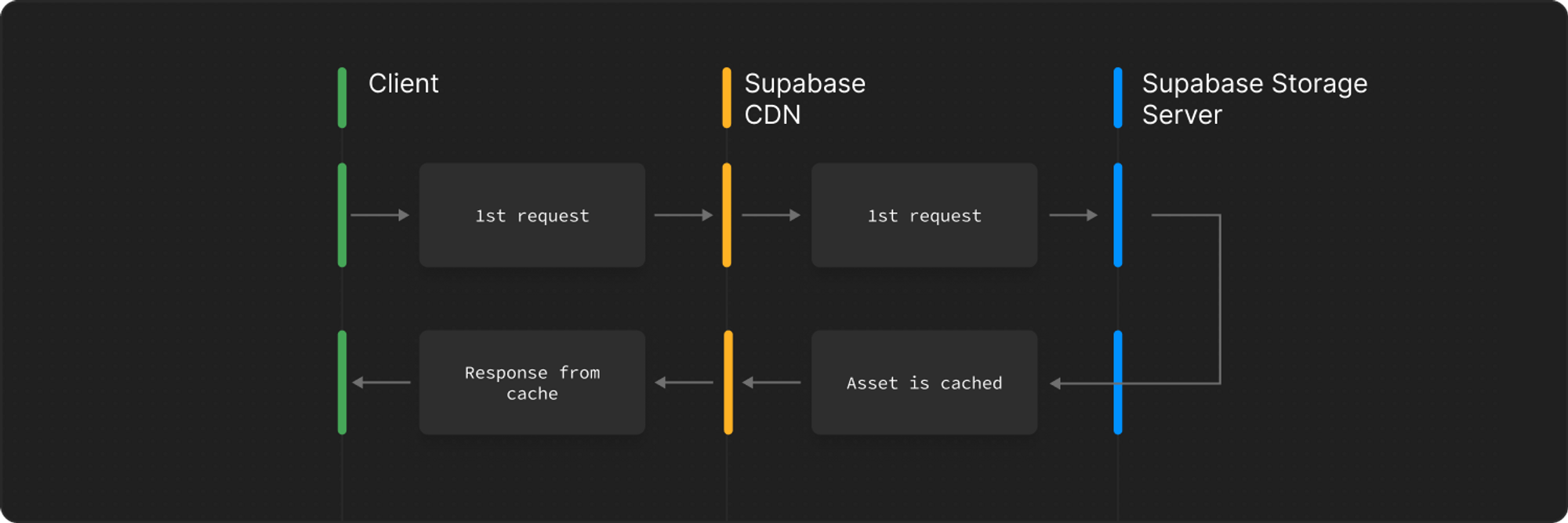
Another user, also in the United States, requests the same object and is served directly from the CDN cache in the United States instead of routing the request back to Singapore.
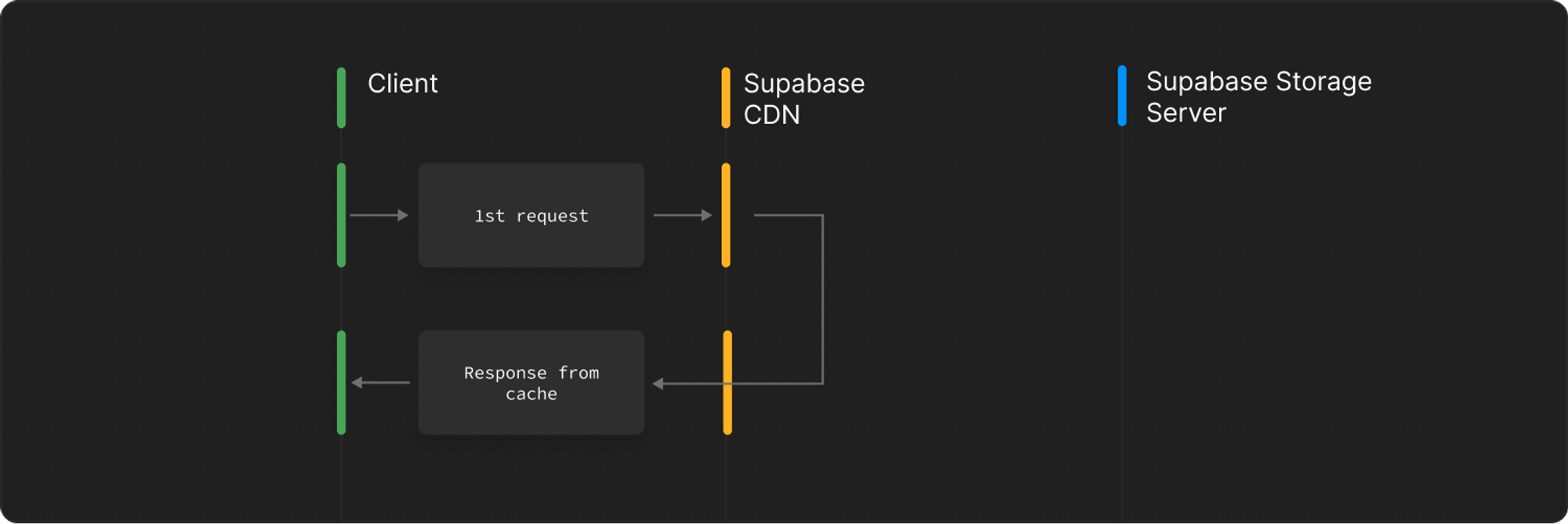
Note that CDNs might still evict your object from their cache if it has not been requested for a while from a specific region. For example, if no user from United States requests your object, it will be removed from the CDN cache even if we set a very long cache control duration.
The cache status of a particular request is sent in the cf-cache-status header. A cache status of MISS indicates that the CDN node did not have the object in its cache and had to ping the origin to get it. A cache status of HIT indicates that the object was sent directly from the CDN.
Public vs private buckets
Objects in public buckets do not require any authorization to access objects. This leads to a better cache hit rate compared to private buckets.
For private buckets, permissions for accessing each object is checked on a per user level. For example, if two different users access the same object in a private bucket from the same region, it results in a cache miss for both the users since they might have different security policies attached to them. On the other hand, if two different users access the same object in a public bucket from the same region, it results in a cache hit for the second user.